Brainstem – the part that connects and acts as a communicator between our brain and our spinal cord. The brainstem itself is composed of midbrain, pons, and medulla oblangata. Even minor injuries or disruptions to this neural communication and this region can have devastating consequences.
The pons is a horseshoe-shaped structure within the brainstem, located under the midbrain and above the medulla oblongata. From the Latin word pōns, meaning “bridge”, this structure serves as a hub for connections between the forebrain and the cerebellum—a structure important for motor control—and the medulla oblongata—a structure critical for vital functions, such as breathing.
Consistent with its location, the pons plays an important role in many unconscious functions, such as respiration and digestion. Despite the small size of pons it is a key structure for sensory and motor functions and the sleep-wake cycle.
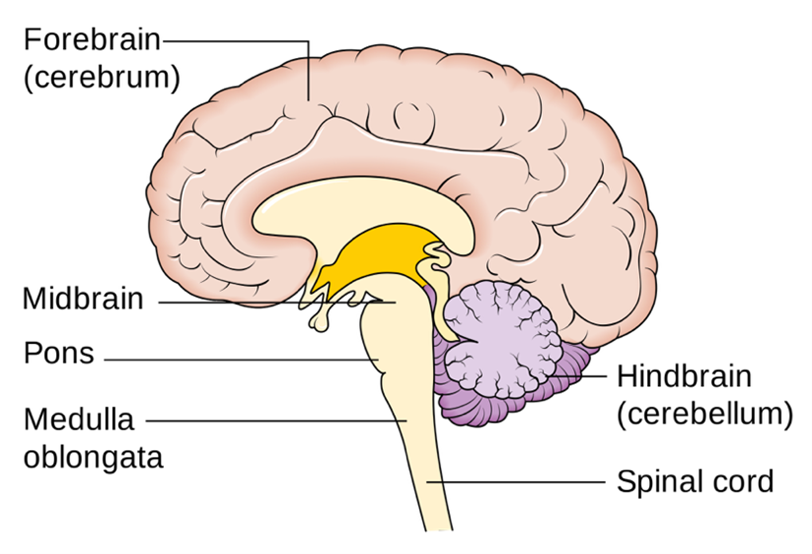
A diagram of the human brain with the Pons labelled. Image courtesy of ThinkFirst.
Certain forms of spinocerebrallar ataxia (SCA) are associated with a loss of neurons in particular regions of the pons. For example, patients with SCA types 1, 2 and 3 have degeneration in the reticulotegmental nucleus, a group of cells that lines the top of the pons. This loss of cells worsens over the course of the disease, resulting in lower pons volume.
Spinocerebrallar ataxia is also associated with changes in the concentration of particular chemicals within the pons, and these changes may appear in early stages of the disease. Based on these findings, scientists may be able to use structural and neurochemical changes to the pons as non-invasive biomarkers to detect different types of spinocerebrallar ataxia and to monitor its progression. Changes to pons structure and function may also be targets for therapies to treat spinocerebrallar ataxia. Understanding the causes of these changes to the pons can also help scientists understand the mechanisms underlying spinocerebrallar ataxia and develop improved strategies to manage the disease.
If you would like to learn more about the pons, take a look at these resources by The Cleveland Clinic and Neuroscientifically Challenged.
Snapshot Written by: Asmer Aliyeva
Edited by: Dr. Chloe Soutar

Snapshot: What is FGF14?
FGF14 or fibroblast growth factor 14 is an essential protein found predominantly in the brain, specifically in Purkinje cells. These brain cells are responsible for maintaining everyday functions such as Read More…
Snapshot: ¿Qué es una Mutación De Novo?
Para que nuestro cuerpo funcione de manera saludable, es necesario llevar a cabo muchos procesos celulares esenciales regulados por moléculas creadas en nuestro interior. Esta molécula base es llamada ADN, Read More…

Snapshot: What is the cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome (CCAS) scale?
Cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome (CCAS) is a condition where cognitive and emotional abilities are affected due to cerebellar damage. Historically, the cerebellum was identified as the part of the brain Read More…



