Snapshot: What is Articulation?
Articulation refers to the ability to produce speech sounds using the tongue, lips, jaw, and the roof of your mouth. All of these organs are also known as articulators. The Read More…
NAF has launched a petition on Change.org calling on the FDA to prioritize treatment options for rare diseases with urgent unmet needs, including Spinocerebellar Ataxia (SCA).
SIGN THE PETITION
A collection of resources for individuals and families affected by ataxia caused by TBI.
A Traumatic Brain Injury can sometimes result in difficulties with balance, coordination, and speech. This condition is called ataxia. Ataxia caused by Traumatic Brain Injury is an acquired form of ataxia, meaning that the ataxia symptoms are the result of an injury or illness.
For complete information about symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of Ataxia, visit our What is Ataxia? page. This page contains NAF’s resources that are specific to Ataxia caused by Traumatic Brain Injury. You can also learn more about Traumatic Brain Injuries through the Brain Injury Association of America.
Sign up for our mailing list to stay up-to-date on Ataxia news.
Presented by Scott Barbuto, MD, PhD
This webinar covers the causes and symptoms of ataxia caused by TBI, the typical diagnostic journey for those affected, what to expect for clinical care, and an overview of current research into the disease.
NAF offers webinars on many topics to help you live better with Ataxia. Visit www.ataxia.org/webinars to find other helpful presentations.
Participating in a research study or clinical trial is one way to take an active role in furthering understanding and treatment of Ataxia. It is also a way to get access to new treatment options before they are widely available. To find studies that are enrolling patients, visit our Help Develop New Treatments page.
A Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is an injury by an external force that affects how the brain works. This happens when the head hits something, something hits the head, or a jolt suddenly causes movement in the brain. Common causes of TBI include falls, motor vehicle accidents, sports, assault, and combat.
Anyone can have a TBI. TBI may be classified as mild, moderate, or severe depending on how intense the initial injury is. Mild TBI is more commonly referred to as a concussion. Sometimes people with TBI develop ataxia, depending on what areas of the brain were injured.
People with other forms of Ataxia usually have worsening symptoms following a TBI. There is limited research on how Traumatic Brain Injury impacts those who already have issues with their cerebellum.
TBI symptoms can vary between different people. Common symptoms of TBI may include loss of consciousness, vomiting, fatigue, slurred speech, and memory loss. Symptoms may appear immediately, but they could also start hours or days after the injury. It is important to get to a hospital as quickly as possible if you suspect someone has had TBI.
Long-term Ataxia symptoms caused by TBI can vary. It depends on what regions of the brain were injured. Three main groups of symptoms can happen – motor, vestibular, and cognitive.
Motor symptoms include problems with balance, coordination, and dexterity. Vestibular symptoms include trouble with eye movement (such as blurry, shaky, jumpy, or double vision), as well as dizziness and vertigo. Cognitive symptoms include changes in intellectual sharpness, emotional regulation, and social awareness.
For mild TBI, most people have symptoms decrease 2-3 weeks after their injury. In some cases, symptoms persist for longer. It can be hard to predict how ataxia caused by TBI will progress over time. This is due to the variability of symptoms. However, with proper support and treatment, improvement is possible.
There are also rehabilitation strategies to help treat ataxia symptoms, including exercise, physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy. Medications may also help treat motor, vestibular, and cognitive symptoms.
A neurologic examination can determine whether a person has TBI and/or Ataxia symptoms. This testing is usually done by a family doctor, emergency room doctor, or neurologist. Some community programs train people to recognize the first signs of TBI, such as sports coaches, life guards, or teachers. It is important to go to the hospital to confirm a TBI diagnosis with a medical professional.
Due to the variety of TBI symptoms, follow up testing may look different from individual to individual. Some potential follow-up tests include MRI brain imaging or CT brain imaging.
SCAsource provides Ataxia research news, directly from researchers to the Ataxia community. Visit SCAsource to see their full collection. Here is a collection of articles about ataxia caused by TBI.

Articulation refers to the ability to produce speech sounds using the tongue, lips, jaw, and the roof of your mouth. All of these organs are also known as articulators. The Read More…

Speech intelligibility refers to how many words can be correctly understood by a listener. For example, if someone says the phrase, “My name is John,” and a listener hears, “My Read More…

Brainstem – the part that connects and acts as a communicator between our brain and our spinal cord. The brainstem itself is composed of midbrain, pons, and medulla oblangata. Even Read More…

Nystagmus, also known as ocular ataxia, is a term that refers to uncontrollable eye movement- usually a repetitive cycle of slow movement in a specific direction followed by a quick Read More…
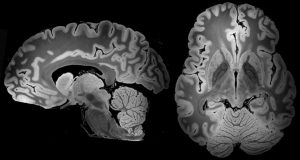
What is it? Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a type of technology used to take detailed pictures of the body. It is commonly used to detect abnormalities in the body, Read More…
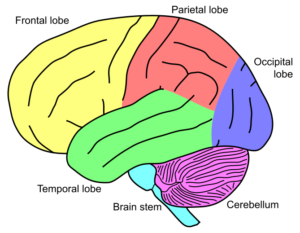
The cerebellum, often referred to as the “little brain”, is part of the brain that is located behind the cerebrum (forebrain). The cerebellum accounts for about 10% of the brain’s Read More…
Our generous donors help us fund promising Ataxia research and offer support services to people with Ataxia. Your gift today will help us continue to deliver on our mission to improve the lives of persons affected by Ataxia.
Join for FREE today! Become a part of the community that is working together to find a cure. As a member you will receive access to the latest Ataxia news with our e-newsletter and Generations publication.
