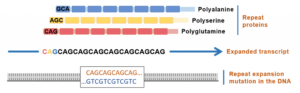
Snapshot: What is RNAi?
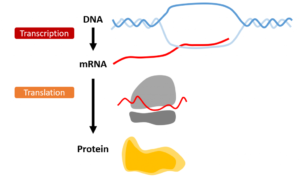
RNA interference, or RNAi, is a natural biological process that inhibits the expression of a specific gene. In medicine, targeted RNAi therapies can be used to silence the expression of a disease-causing gene. To understand RNAi, you first have to understand RNA. An overview of RNA is the messager between Read More…